[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Bottle Fly
The common green bottle fly is distinguished by its metallic bluish-green or goldish coloring. These flies are slightly larger than the common house fly and are normally 10-14mm long. Bottle flies prefer warm and moist climates and prefer to feed and reproduce on meat, fish, animal corpses, open wounds, or excrement.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]
Cluster Fly
The cluster fly is a type of blowfly that can often be a household nuisance, especially in late summer or fall when they enter houses to hibernate. These flies do not lay eggs in human food, and they are solely parasitic on earthworms. The cluster fly is about 7mm long and is distinguished by lines or stripes behind the head and short golden hairs on the thorax.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]
Crane Fly
The crane fly is a slender, long-legged fly that can vary in length from 2-60 mm. These flies are weak fliers and can be easily caught. Females carry their eggs on their abdomen, so they may appear larger than the males. Females also have a pointed abdomen that appears to be a stinger, but is actually harmless. They flies do not bit humans[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]
Flesh Fly
The flesh fly is a species of fly that feeds on, and lays its eggs in, the flesh of dead and decayed animals. Their larvae, commonly known as maggots, live for 5-10 days before maturing into adulthood where they will live for 5-7 days.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]
Fruit Fly
The common fruit fly has red eyes and is yellow in color with black rings across the abdomen. These flies are about 2.5mm long. Fruit flys get their name because they lay their eggs in plant tissues. These flies also have a short lifespa, most live for less than a week.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]
Fungus Gnat
The fungus gnat is a small, dark fly that is about 2-5 mm long when mature. Fungus gnat larvae feed on plant roots or fungi, and adults are crucial to the process of spreading mushroom spores and plant pollen. These gnats are often attracted into homes when plants are overwatered. They often don’t cause much harm to health plants, but can severely damage seedlings.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]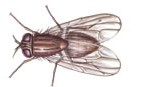
House Fly
The house fly is the most common of all domestic flies and accounts for about 90% of flies inside human habitations. These flies are distributed throughout the world and can carry a variety of pathogens, such as typhoid, cholera, and salmonella. House flies are 8-12 mm long and have a gray thorax with four dark lines on their back. The female house fly will lay about 500 eggs in a lifetime. These eggs will hatch within a day and feed on organic material, such as garbage and feces.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]
Moth Fly
The moth fly is a short and hairy fly that gives them a moth-like appearance. This species prefer more arid regions and are therefore also known as sand flies. These flies can also transmit various tropical diseases.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”” parallax=”” parallax_image=””][vc_column width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]
Phorid Fly
The phorid fly is a species of hump-backed flies that prefer running over flying. They are about 1/4in long and range in color from black or brown to yellow. These flies are found worldwide, but they are commonly found in tropical areas. Several species of the phorid fly have been introduced in the US to help control the fire ant population since phorid flies reproduce by laying eggs in the thorax of the ant.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
